Development of Multi-sensor That Detects Glucose and Lactic Acid in Sweat
- admin
- 2023-03-10
- 2292
Professor Jae-young Park's Research Team Develops a Multi-sensor
That Detects Glucose and Lactic Acid in Sweat
- Development of ‘hybrid Nanoporous Carbon’ Deposited 3d Graphene Flexible Electrode Technology -
- Development of Ultra-sensitive and Broadband Real-time Monitoring Multi-sensor for Sweat Sugar and Lactic Acid -
- Significantly Improved Sweat Sensor Accuracy Through Integration of Temperature and Ph Compensation Sensors -
Professor Jae-Young Park (Department of Electronic Engineering) research team at our school coated laser-induced graphene (LIG) with hybrid nanoporous carbon (H-NPC) material having a core-shell structure on a polymer flexible substrate, resulting in flexible biomaterials with excellent electrical, mechanical, and chemical properties. The team succeeded in developing a high-performance patch-type biosensor that can detect and monitor sugar and lactic acid in electrodes and human sweat in real time.

<Professor Jaeyoung Park (Left) and Ph.D. student Asa Dujaman (Right)>
This study was conducted by the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology Industrial Technology Innovation Project (20000773, development of patch-type nanomulti-sensor innovation technology for monitoring non-blood-based metabolic syndrome) and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy's Industrial Technology Innovation Project? (RS-2022-00154983, low-power sensor and It was performed with the support of self-supporting power sensor platform development). It was published in the Biosensor & Bioelectronics Journal (IF: 12.545), the world's top international SCI journal in the biosensor field of Elsevier Publisher.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0956566322008867
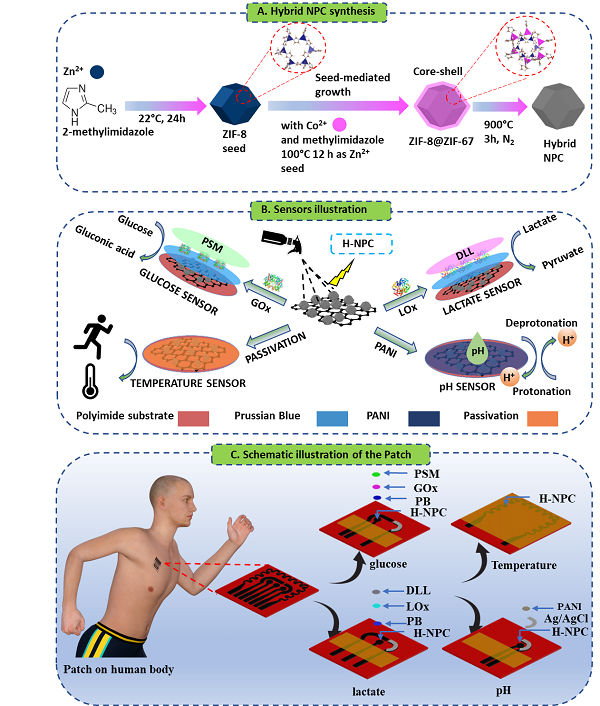
<H-NPC (Hybridized Nanoporous Carbon) Material Synthesis Procedure and Glucose, Lactic Acid, Temperature, pH Integrated Multisensor Patch Conceptual Diagram>