Prof. Nam-young Kim's Research Team Successfully Develops a Sensor for Detecting COVID-19 Antigens
- admin
- 2024-09-13
- 1827
· Professor Nam-young Kim's Research Team (Department of Electronic Engineering) Successfully Develops
Wooded Quoit Conformation Structural Aptamer-based Sensor for
Detecting COVID-19 Variant Antigens in Patients
- Published in the scientific journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics
(JCR 1.5% Q1, IF: 12.545) -
- Successful development of an aptamer-based biosensor for detecting
COVID-19 variant antigens -
A research team led by Professor Nam-young Kim from the Department of Electronic Engineering, along with Dr. Parshant Kumar Sharma (first author) from the same department, has announced the successful development of an aptamer-based biosensor for detecting COVID-19 variant antigens.

(Left)
Dr. Parshant Kumar Sharma (Right) Professor Nam-young Kim
The COVID-19 pandemic
and its ongoing spread pose a serious threat to public health, as variants of
the coronavirus, known as SARS-CoV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
Coronavirus 2), continue to undergo genetic changes. These changes can affect
the severity of symptoms, the effectiveness of vaccines, and the
transmissibility of the virus. In point-of-care diagnostic analysis, specific
gene or protein sequences exclusive to each variant can be identified.
Currently, ultra-fast,
responsive, and accurate antibody detection faces several challenges. The
research team developed a chip capable of ultra-fast (within 5 seconds) and
low-cost (0.15 USD) analysis, using label-free detection of SARS-CoV-2 S
(Spike)/N (Nucleocapsid) proteins and other variants in actual patient samples,
with excellent performance in manufacturing, implementation, and detection. A
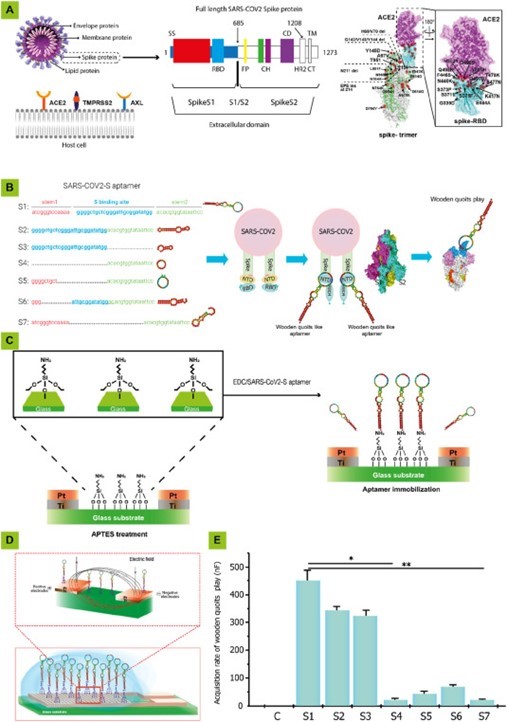
label-free DNA aptamer capacitive biosensing device was used to detect
SARS-CoV-2 variants. The new cutting-edge biosensing device developed a WQCSA
(Woodenquits Conformative Structural Aptamer)-based interdigitated capacitor
electronics (WQCSA-IDCE) system. The WQCSA-aptamer was used as a switch-on
response to achieve ultra-sensitivity in the variable region of SARS-CoV-2 and
was used to measure the fluorescent SARS-CoV-2 S/N proteins. The developed
sensor can be used with various types of label-free DNA aptamers, functioning
as a rapid, cost-effective, and label-free biosensor for a range of severe
acute respiratory syndrome diseases.
[Aptamer-Based
Biosensor for Detecting COVID-19 Variant Antigens]
This research was supported by the National
Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Priority Research Centers Program and Basic
Science Research Program funded by the Ministry of Education
(2018R1A6A1A03025242, 2018R1D1A1A09083353, and 2022R1A2C209333612). The research results were published in the internationally renowned
journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics (IF=12.545) by Elsevier, under
the title 'SARS-CoV-2 Detection in COVID-19 Patients' Samples using Wooden
Quoit Conformation Structural Aptamer (WQCSA)-Based Electronic Bio-sensing
System.' (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2024.116506)
?